Fertility Medication
We prepared a special guide for the main medications connected with fertility treatments.
FERTILITY MEDICATIONS
Lupron Suppression Protocol
Lupron suppression IVF protocol begins with the patient taking birth control pills for 14-21 days to synchronize egg development. During the last 2-3 days of oral contraceptives, we use another fertility medicine called leuprolide acetate (Lupron) to suppress the pituitary gland and prevent premature ovulation.
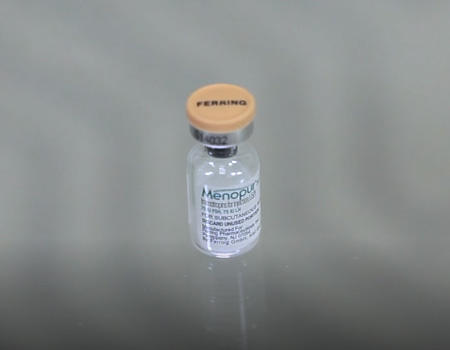
After about 10 days of Lupron, the ovaries are suppressed and we initiate gonadotropins like follicle stimulating hormone (FSH; eg, Gonal-F, Follistim, Bravelle) and human menopausal gonadotropins (Menapur) to stimulate the egg development. We continue Lupron and gonadotropins for about 8-12 days until the eggs reach maturity. During this time, the stimulation is monitored with a pelvic ultrasound and blood test measurements of estradiol every 2-3 days.
Once the follicles (egg) reach maturity, an injection of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) is given to induce ovulation and the follicles are retrieved 36-38 hours later. Progesterone supplementation is initiated the day after retrieval and continued for two weeks until the pregnancy test.
AFCT works closely with Lisanne Wellness Center (LWC) to offer wellness services that regulate the body and enhance infertility treatments. Thanks to our unique Mind and Body approach to fertility success that includes detoxification, meditation, nutrition, and our well-renowned fertility specialists, we have been able to reach an excellent 78% pregnancy success rate! (The national average is 48.5%)
FERTILITY MEDICATIONS
Antagonist Protocol
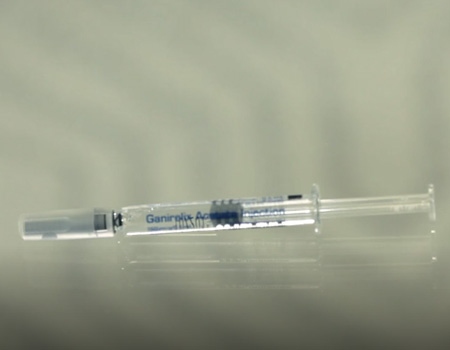
In this protocol, we follow ovarian follicle (egg) synchronization with birth control pill for about 14-21 days. We initiate gonadotropins (follicle stimulating hormone [FSH], human menopausal gonadotropins) to stimulate egg development for about 8-12 days. In the middle of the cycle we typically initiate honadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) antagonist such as cetrotide, which acts rapidly to suppress the pituitary gland and prevent premature ovulation.
The antagonist is administered daily until the follicles reach maturation and human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) is given to induce ovulation. The eggs are retrieved 36-38 hours later. We prefer to use this protocol in women who are high responders (eg, those with polycystic ovarian syndrome) and egg donors who are known to have several ovarian follicles on their initial ovarian assessment.
With this protocol, we are able to utilize “Lupron trigger” where we can induce ovulation with leuprolide acetate and minimize the potential complication of ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (ovarian enlargement and sometimes fluid accumulation in the abdomen).
FERTILITY MEDICATIONS
Microdose Lupron Flare Protocol
In patients with low ovarian reserve, we initiate gonoadotropins (follicle stimulating hormone [FSH] and human menopausal gonadotropins) around day 2 of the menstrual cycle. Around day 4 of the menstrual cycle, we add a small amount of leuprolide acetate called a “microdose flare,” which is given twice daily in order to stimulate the pituitary gland natural release of follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) and leutinizing hormone (LH). This combination seems to help reinforce the ovarian follicle development.
The use of fertility medicine/drugs to stimulate growth
and maturation of follicles (eggs) in the ovaries.
Here are some of the most common fertility medicine used during IVF or OI treatment:
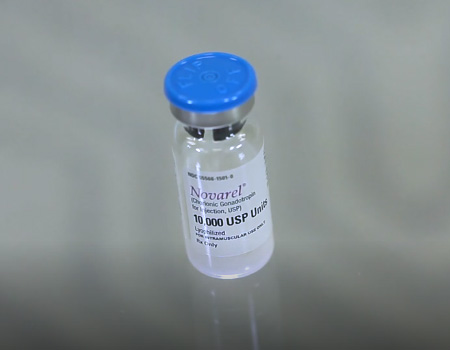
Leuprolide (Lupron), Nafarelin Acetate (Synarel), Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH), Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (hCG, Novarel), Progesterone, Demerol, Diazepam (Valium), Xylocaine, Aspirin, Methylprednisolone (Medrol), Cetrotide, Repronex, combination of FSH and LH and other medications.
FSH
Sold under commercial name Gonal-F, Follistim or Bravelle
Used to stimulate the development of multiple eggs in the ovaries. Mild degrees of ovarian overstimulation are common side effects of this medication. Overstimulation is characterized by abdominal bloating, weight gain (due to body fluid retention) and mild to moderate pelvic and/or abdominal discomfort.
This is a self-limiting condition and does not require treatment. Severe ovarian overstimulation is rare. The swollen ovaries can cause moderate to severe pain usually lasting a few days. You could have significant body fluid retention, especially within the abdominal cavity.
In its most severe forms, ovarian overstimulation could result in ovarian rupture requiring major abdominal surgery, thickening of blood causing shock or formation of a blood clot in a blood vessel, or even death. The number of patients with such severe ovarian overstimulation is very small; a few out of the thousands of treated patients. Localized skin reaction at the injection site may occur.
LH + FSH
Sold under commercial name Menopure or Repronex
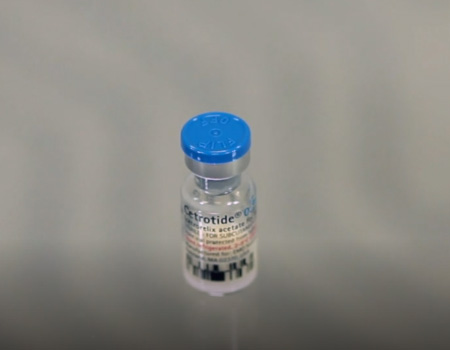
Cetrotide®
A new generation gonadotropin releasing hormone (GnRH) antagonist used to prevent a premature ovulation in controlled ovarian stimulation prior to assisted reproductive technologies. This medicine comes in a powder form as well as with a prefilled syringe.
Lupron or Synarel
Used to prevent premature ovulation. They have minimal, if any, side effects, most commonly transient headaches, possible hot flashes and body fluid retention. Localized skin reaction at the injection site may occur.
hCG
Necessary for the final stages of eggs maturation. It is also used to increase the probability of embryo implantation. The hCG can contribute to ovarian overstimulation. Localized skin reaction at the injection site may occur.
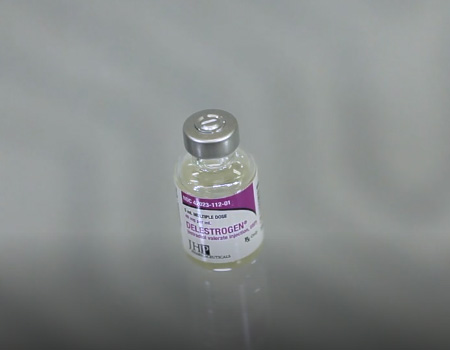
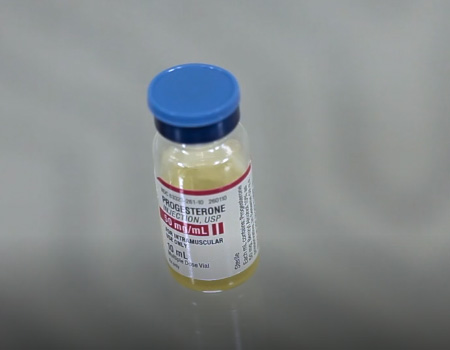
Progesterone in Oil of Ethyl Oleate
Sold under commercial Menopure or Repronex
Used to supplement your own progesterone production. It is given as intramuscular injection or as a vaginal capsule (suppository).
Fertility Medicine That Come In Pill Form
Doxycycline
is a broad spectrum antibiotic used to eliminate possible bacterial contamination of the semen and the uterine cavity. Very few people are allergic to Doxycycline. A common side effect is transient nausea and possible vomiting, especially if the medication is taken on an empty stomach. Since photosensitivity manifested by an exaggerated sunburn reaction has been observed with the Doxycycline, you should avoid excessive sun exposure.
Medrol
is a corticosteroid. It is given in a small dose to protect embryos from being attacked by immune cells. It is given only if the eggs or embryos are micro manipulated.
Vicodin
Valium
is a corticosteroid. It is given in a small dose to protect embryos from being attacked by immune cells. It is given only if the eggs or embryos are micro manipulated.
Vivelle dot
is an estrogen patch that is used after the embryo transfer to help with the embryo implantation. It is applied to the lower abdomen and sticks like a band-aide. You can shower with the patch on.
Allergic Reactions
Possible allergic reactions to all of the aforementioned medications include rash, fever, itching, difficulty in breathing (asthma), or shock Allergic reactions are quite rare.
Long Term Risks
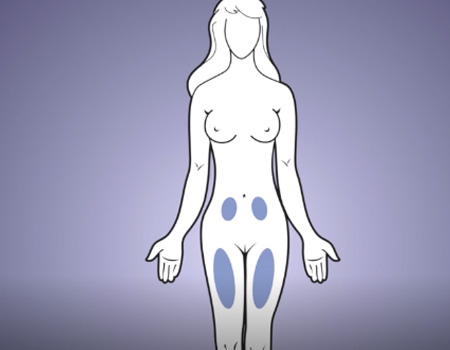
Injection Training Videos
Dr. Michael Allon
Dr. Dmitri Dozortsev